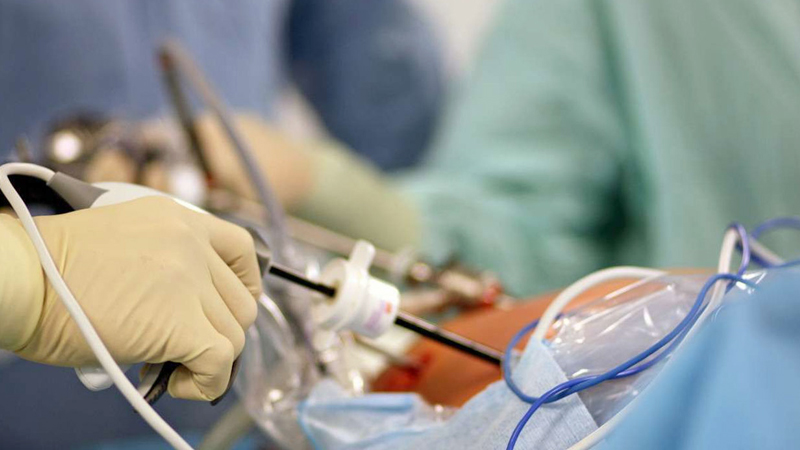
PEG Tube Insertion
PEG (percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy) tube insertion is a medical procedure used to place a feeding tube into the stomach through the abdominal wall. It is commonly performed for patients who are unable to eat or swallow food and require long-term nutritional support.
Here's an overview of the PEG tube insertion process:
Preparation: Before the procedure, the patient is usually asked to fast for a certain period of time to reduce the risk of aspiration (inhaling stomach contents into the lungs). The patient's medical history, including any allergies or medications, is reviewed, and blood tests may be conducted to assess clotting function.
Anesthesia: PEG tube insertion is typically performed under sedation or general anesthesia to keep the patient comfortable and relaxed during the procedure. The level of sedation depends on the patient's medical condition and the preference of the healthcare provider.
Insertion: During the procedure, an endoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera at its tip) is inserted through the mouth and guided into the stomach. The endoscope allows the healthcare provider to visualize the inside of the stomach and identify the best location for the PEG tube insertion.
Gastric puncture: Once the optimal location is identified, a needle is inserted through the abdominal wall into the stomach under endoscopic guidance. This creates a passage (stoma) between the skin and the stomach wall.
Guidewire placement: A thin, flexible guidewire is passed through the needle and into the stomach. The endoscope is then withdrawn, leaving the guidewire in place.
Dilation: The size of the stoma is gradually enlarged using a series of dilators passed over the guidewire. This creates a space large enough to accommodate the PEG tube.
Tube placement: Once the stoma is dilated, the PEG tube is threaded over the guidewire and into the stomach. The internal bumper of the tube keeps it securely in place within the stomach, while the external portion of the tube extends out through the abdominal wall.
Securing the tube: The external portion of the PEG tube is secured to the skin using a disc or bumper, and a dressing is applied to the site to keep it clean and dry.
Confirmation: After the tube is inserted, its placement is confirmed by visualizing its position within the stomach using the endoscope or by aspirating stomach contents through the tube and checking the pH.
After the procedure, patients are monitored for a period of time to ensure there are no immediate complications. They are provided with instructions on how to care for the PEG tube and how to administer feedings and medications through the tube. Follow-up appointments are typically scheduled to monitor the patient's progress and address any concerns.
